- Homepage
- >
- Scientists
- >
- Research topics
- >
- Nuclear physics
- >
- FIRE
Research topics
- Nuclear physics
- Overview of the research topics
- FINDS
- FIRE
- STARS
- DOSADO
- PHASE
- THEORY
- DELPH
- GTA
- Interdisciplinary research
FIRE
The FIRE (FIssion and REactions) group is composed of 6 permanent physicists and several doctoral and post-doctoral researchers. The main focus of the group’s research is nuclear dynamics induced by heavy-ion collisions, from the Coulomb barrier to Fermi energies and beyond, up to a few hundreds of MeV per nucleon. These reactions allow to address a broad range of topics, including (but not limited to):
- interplay between nuclear structure effects, dissipation and the dynamics of large-amplitude deformation, in the fission process;
- comprehensive understanding of fission throughout the nuclear chart;
- evolution of nuclear reactions with bombarding energy from Coulomb barrier energies, to dynamical break-up and multifragmentation at Fermi energies, and beyond, towards the participant-spectator regime;
- constraining the equation of state of nuclear matter over a wide range of densities and isospin asymmetries (N≠Z), including clusterization effects at sub-saturation densities.
Experiments performed by the group are mostly carried out at GANIL, but also at other facilities worldwide, such as GSI/FAIR (Germany), LNS (Italy), and FRIB (USA). In addition, the FIRE group plays a key role in supporting the experimental programme at GANIL, with responsibilities for two major instruments of the facility:
- The scientific coordination of the VAMOS++ magnetic spectrometer. The group is engaged in a major programme of research, FISSION@VAMOS, for the isotopic identification of fission fragments produced in fusion or multi-nucleon transfer reactions in inverse kinematics. From 2029 onwards, the return of AGATA to GANIL (for campaigns with GRIT and VAMOS) opens the possibility for transfer reactions studies and future fission experiments coupling the identification capabilities of VAMOS++ with high-resolution gamma ray spectroscopy.
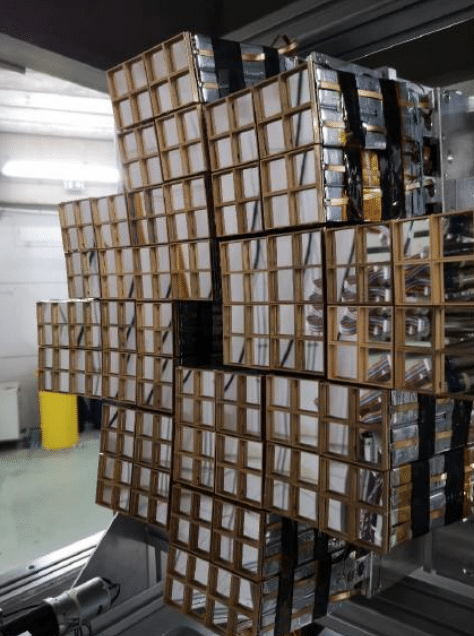
- The FAZIA charged particle identification array, currently coupled with the INDRA multi-detector, is managed in close coordination with the Nuclear Thermodynamics group of LPC Caen, in the framework of an international collaboration. FIRE group members lead ongoing research using this coupling into the nuclear equation of state and clustering in light nuclei.