- Homepage
- >
- Scientists
- >
- Research topics
- >
- Nuclear physics
- >
- GTA
- Nuclear physics
- Overview of the research topics
- FINDS
- FIRE
- STARS
- DOSADO
- PHASE
- THEORY
- DELPH
- GTA
- Interdisciplinary research
GTA
The GTA (Groupe des Techniques des Acquisitions) group is dedicated to supporting nuclear physics research by ensuring the optimal operation of data acquisition systems designed to analyze the products of nuclear reactions within the GANIL experimental areas. Comprising around fifteen members, our team brings together a core of ten permanent staff (engineers, researchers, and technicians) alongside fixed-term contractors, apprentices, and interns, fostering a dynamic environment where expertise is continuously shared and enhanced.
We primarily serve experimental physicists and the nuclear physics research community, playing a key role in the reliability and efficiency of the technical infrastructures that underpin their work. Our missions span the entire lifecycle of acquisition systems, from design to modernization, covering both hardware (digitization electronics, high-precision timestamping, event selection) and software (control-command tools, data flow management, equipment configuration). We also provide operational support, including on-site technical assistance (with 24/7 on-call availability for emergencies) and training to ensure proficient use of our systems.
Our work materializes in integrated data acquisition solutions: specialized systems, custom software for control and analysis, and innovative electronic boards, all tailored to the demanding requirements of experiments. Beyond these technical deliverables, we offer human expertise, personalized support, and constant responsiveness, enabling researchers to focus fully on their scientific advancements with high-performance, reliable tools.
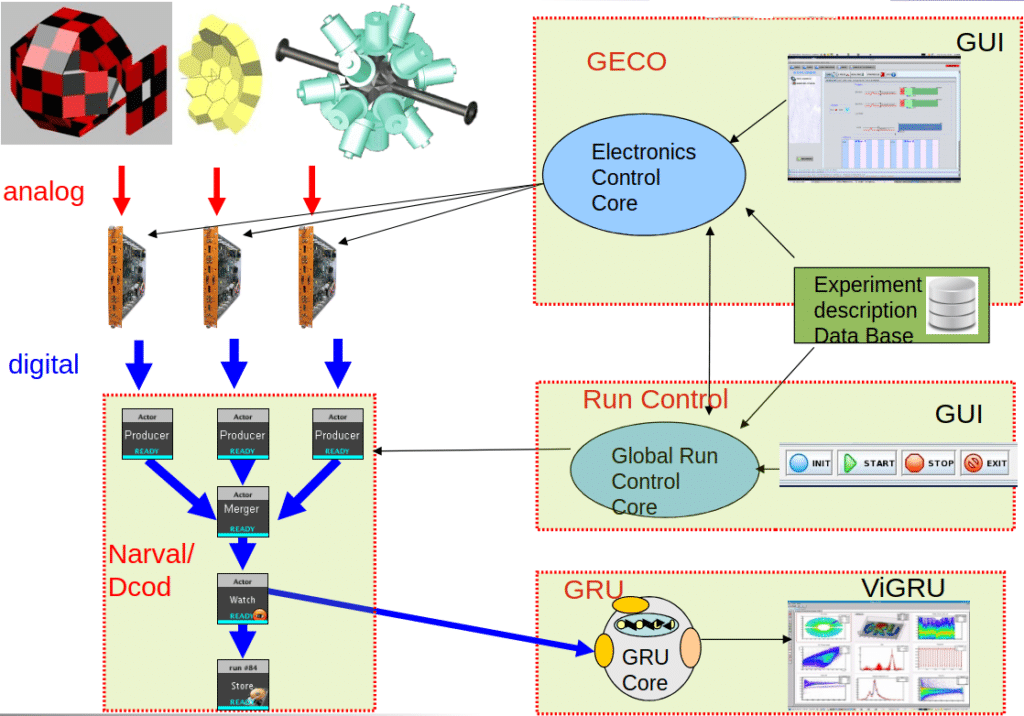
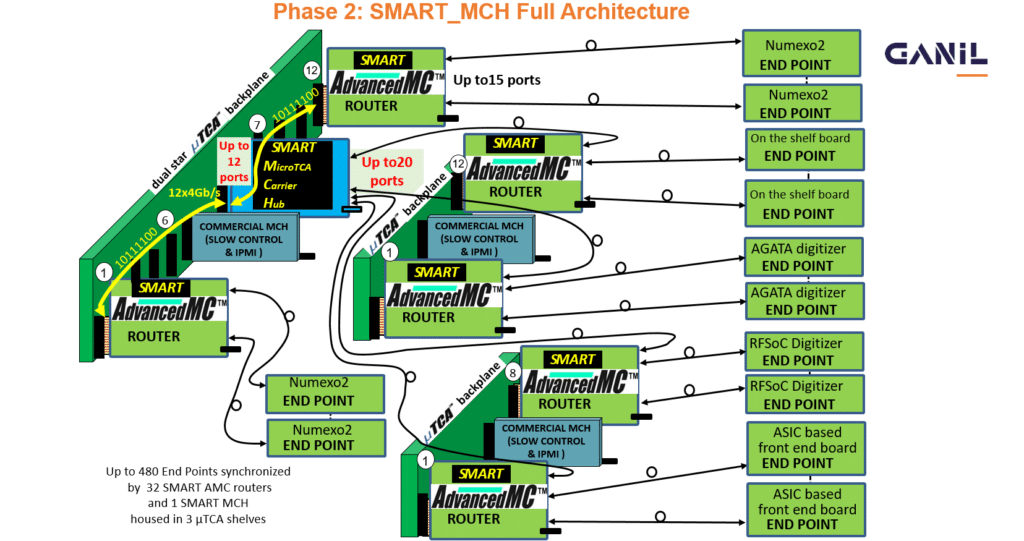
Two home-made flagship examples illustrate our approach: The NumExo2 digitization module, which embeds signal processing directly in the FPGA, ensures optimized data acquisition, while our acquisition chain collects and aggregates this data alongside inputs from other digitizers (often linked to additional detectors). Control and monitoring are handled by a suite of in-house software, designed to adapt to the diverse electronics of a single experiment. These digitizers are synchronized to a common time reference via the SMART system, whose tree-based architecture enables precise timestamping across all detection systems. The structure consists of a central hub module (time reference source) connected to multiple router modules, which in turn link to hundreds of endpoint modules (across various detectors), ensuring rigorous temporal alignment between all experimental components.
Acronyms:
GTA: Groupe des Techniques des Acquisitions (en.: data Acquisition Technics Group)
FPGA: Field-Programmable Gate Array
SMART: SFP connectivity and MicroTCA for Advanced Remote Trigger