- Homepage
- >
- Scientists
- >
- GANIL-SPIRAL 2 facilities
- >
- Instrumentation
- >
- REGLIS3
- Accelerators
- Available beams
- Experimental areas
- ARIBE
- D1
- D2
- D3-D6 / LISE
- D5
- DESIR
- G1 / VAMOS
- G2
- G3
- G4
- IRRSUD
- LIRAT
- NFS – Neutrons for Science
- S3 – Super Separator Spectrometer
- Instrumentation
- ACTAR TPC
- AGATA
- CHATEAU DE CRISTAL
- DIAMANT
- EXOGAM / EXOGAM2
- FAZIA
- INDRA
- LPCTrap
- MUST2
- NEDA
- PARIS
- REGLIS3
- S3 Low Energy Branch
- SIRIUS
REGLIS3
We propose the development of a new generation of an integrated ion source system for the production of very pure radioactive ion beams at low energy, including isomeric beams. This ion source is also, in its own right, an experimental tool for laser spectroscopy. The Rare Elements in-Gas Laser Ion Source and Spectroscopy (Reglis) device will be installed at the S3 spectrometer at the Ganil laboratory in Caen.
Reglis will be a source for the production of new and pure radioactive ion beams at low energy as well as a spectroscopic tool to measure hyperfine interactions, giving access to charge radii, electromagnetic moments and nuclear spins of exotic nuclei so far not studied. Owing to the unique combination of such a device with the radioactive heavy-ion beams from S3, a new realm of unknown isotopes at unusual isospin (N/Z ratio, referred to as exotic isotopes) will become accessible. The scientific goals focus on the ground-state properties of nuclei with an equal number of protons and neutrons (N=Z) up to the doubly-magic 100Sn (Z=N=50) and those of the very heavy and superheavy elements near and beyond fermium (Z=100). It is our goal to develop this new, efficient, and universal source for pure beams and for performing high-resolution laser spectroscopy that will overcome the present experimental constraints to study very exotic nuclei.
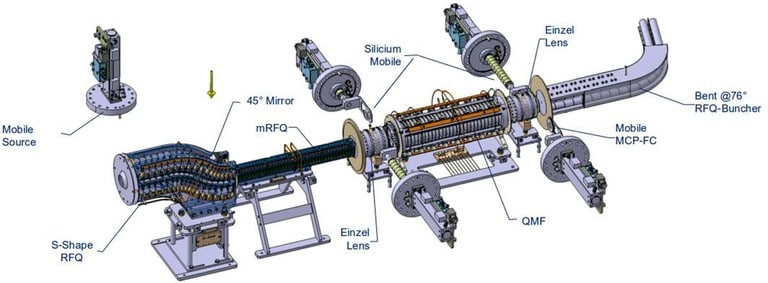
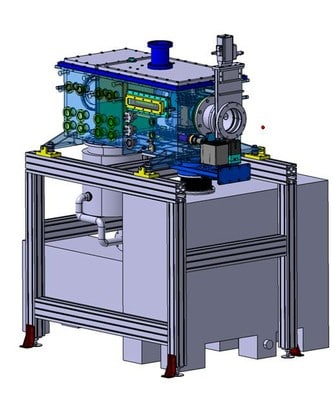
The beam from S3 is stopped in argon buffer gas. It is guided by the gas flow towards a Laval nozzle, where a supersonic jet is formed. The particles are resonantly ionised by laser light in the gas jet. They are captured in a sequence of radiofrequency quadrupoles (RFQ), where they are cooled and bunched before being sent into the experimental set-up downstream.
The design and construction of Reglis are on schedule. While the last two years were spent on simulation and calculation to define its many parameters, the design of the buffer gas cell, radiofrequency quadrupoles and vacuum chambers has now been completed at IPN Orsay and LPC Caen. First calls for tender related to the pumping system will be published in March 2016. They will be followed soon after by calls for other components. Construction and assembly will start in the forthcoming months. Testing will take place from the Autumn of this year onwards and will continue throughout 2017.
The S-shaped RFQ, which displaces the ionic beam vertically and allows for an axial line of sight to send in the laser beam, is being manufactured at LPC. The particles are transmitted in a second smaller RFQ, which is also being assembled at present. Construction of the quadrupole mass filter (QMF) is foreseen for November. The ion buncher, which furthermore bends the beam towards the experimental set-up, is under study.
A multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrometer for mass measurements of the ions that are produced by Reglis has been developed at Ganil and will be tested this summer. The integration of Reglis at S3 as well as all matters of infrastructure are being coordinated at Ganil. While Reglis will be commissioned with the available Ti:Sa laser system at Ganil, a powerful dye laser system is being validated at a test bench set-up in Louvain in Belgium, where also detailed studies of the atom flow in the supersonic gas jet take place.
Publications
“In-gas laser ionisation and spectroscopy experiments at the Superconducting Separator Spectrometer (S3): conceptual studies and preliminary design”, R. Ferrer et al, Nuclear Instruments and Methods B 317, 570 (2013)
Cell – in and out
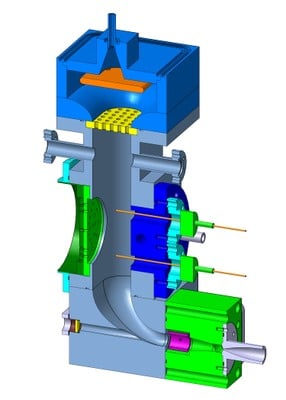 |
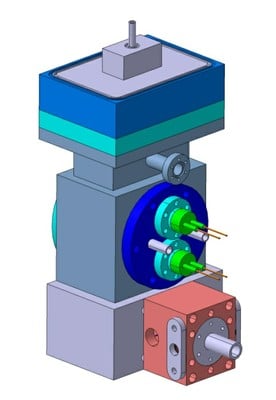 |
The sequence of radiofrequency quadrupoles that captures and bunches the ion beam
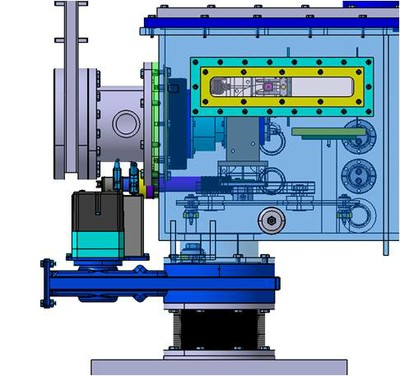
The gas-cell chamber with the entrance window for laser ionisation in the gas jet
 |
 |
Partners
Reglis is a project funded by the French National Research Agency (Agence Nationale de la Recherche – ANR) under the contract n° ANR-13-BS05-0013 with four partners:
France: GANIL, Institut de Physique Nucléaire d’Orsay (IPNO), Laboratoire de Physique corpusculaire de Caen (LPC)
Belgium: KU Leuven
